Nuclear safety and previous damage investigations are jeopardized by years of refusals to investigate nuclear power plant explosions by the NRC, DOE, NEA, and IAEA. The potential scope of this issue is extraordinary with respect to explosion and water hammer damages in nuclear power plants. Yet, government agencies refuse to act.
Explosion and Water Hammer Damages in Nuclear Reactor Systems
Damages in nuclear reactor systems are consistent with explosion damages and water hammer damages. However, I cannot absolutely prove such conclusions in all cases, since nuclear industry regulators and nuclear reactor plant operators block cutting-edge research.
Accordingly, I will list a number of failures in nuclear power plants, which have so-called unknown causes. How can there be unknown causes for major failures in nuclear power plants, where safe nuclear reactor operations are so important?
Explosions fill in the blanks under unknown causes. Not only will regulators and nuclear plants not support my research requests, but those organizations refuse to act on their own to stop explosions and ensure nuclear safety.
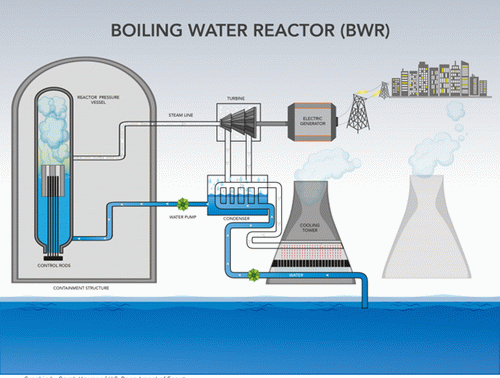
All water-cooled nuclear reactor designs are subject to explosion damages and water-hammer damages. See Figures 1 and 2 for two of the basic designs.
Nuclear Power Plant Explosions during Normal Operations
In a recent Op Ed, PWR explosions were primarily attributed to reactor startups and pressurizer operations, and BWR explosions were primarily attributed to reactor startups, even though other explosion causes are known ("Ringhals 4 and the Next Nuclear Power Plant Explosion Prediction", Click Here). Note that the term startup refers to changing the reactor operating condition to 100% power from cold shutdown, hot shutdown, and low power ("L5. - Low Power and Shutdown PSA", n.iaea.org/Common/topics/OpenTopic.aspx?ID=12768). Even changes in the reactor power level may result in hydrogen explosions if hydrogen is not fully vented from reactors. BWRs and PWRs have been investigated, but other water cooled nuclear reactors have similar explosion dangers.
Nuclear Reactor Fuel Damages
Nuclear fuel damages were also discussed in "Ringhals 4 and the Next Nuclear Power Plant Explosion Prediction" (Click Here). There are multiple causes of fuel damages, where explosions have not been previously considered ("Review of Fuel Failures in Water Cooled Reactors (2006-2015)", click here).
In this IAEA survey for 97% of operating, water-cooled reactor plants, 4 year increments were evaluated for failures. Interpretation of results and probable failure causes follow.
- PWRS - Between 14.6% and 50% of failure causes were unknown (explosion damages).
- PWRS - Between 0.9% and 5.7% of failure causes were cracks (explosion damages).
- BWRS - Between 1.78% and 29.2% of failure causes were unknown (explosion damages?).
- BWRS - Between 9.9% and 34.1% of failure causes were cracks (primarily cavitation damages and some explosion damages).
- Other damages from corrosion, handling, and fretting may be partially attributed to explosions.
- Explosion damages are consistent with fuel bowing damages, which are described in an article by others ("Avoiding BWR Channel Distortion", click here).
- Other fuel assembly-structural damages are consistent with explosion damages as well.
- Vibrations due to fluid flow also cause fuel damages.
Water hammers and explosions were not mentioned at all in this IAEA report. Water hammers have been a known nuclear plant problem for decades, and explosions have been a published nuclear plant concern since 2011 ("Water-hammer Prevention, Mitigation, and Accommodation: A Perspective", .osti.gov/biblio/6871123).
The failure mechanisms for nuclear fuel rods and assemblies are complicated, and this new explosion research further complicates failure analyses.
PWR Reactor Pressure Vessel Damages
Damages to the Davis Besse reactor pressure vessel occurred. Quoting newspapers and an NRC report (Nuclear Regulatory Commission):
On February 16, 2002, the Davis-Besse Nuclear Power Station in Oak Harbor, Ohio, began a refueling outage that included inspecting the nozzles entering the head of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV), the specially designed container that houses the reactor core and the control rods that regulate the power output of the reactor. Of these vessel head penetration (VHP) nozzles, the licensee's inspections focused on the nozzles associated with the mechanism that drives the control rods, known as the control rod drive mechanism (CRDM). Both the inspections and their focus were consistent with the licensee's commitments in response to NRC Bulletin 2001-01, "Circumferential Cracking of Reactor Pressure Vessel Head Penetration Nozzles," which the agency issued on August 3, 2001.
In conducting its inspections, the licensee found that three CRDM nozzles had indications of axial cracking, which had resulted in leakage of the reactor's pressure boundary. Specifically, the licensee found these indications in CRDM nozzles 1, 2, and 3, which are located near the center of the RPV head. The licensee reported these findings to the NRC on February 27, 2002, and provided supplemental information on March 5 and March 9, 2002. The licensee also decided to repair the three leaking nozzles, as well as two other nozzles that had indications of leakage but had not resulted in pressure boundary leakage [Figure 3].' 'The investigation of the causative conditions surrounding the degradation of the RPV head at Davis Besse is continuing' ("Overview of Reactor Vessel Head Degradation", click here).
OAK HARBOR, Ohio - Eight more control-rod-drive mechanism nozzles atop Davis-Besse's nuclear reactor head have indications of cracks or flaws, bringing the number needing repair to 24, FirstEnergy Corp. said Monday.' 'The flaws were in the early stages of becoming cracks, many too small to be seen. Only one nozzle developed a through-wall crack large enough to leak radioactive coolant,' That's more than one third of the head's 69 nozzles.' 'Officials remain puzzled why the device, built to last decades, had problems with its nozzles so quickly' ("8 more nozzles at Davis Besse found to be flawed", Click Here.
Energy Harbor replaced First Energy Corporation as the plant operator, and they did not respond to a request for pressurizer and reactor pressure-vessel temperature and pressure data to further investigate Davis Besse water hammers and explosions. The following email was not answered.
'Pressurizer Information Request / Explosion SafetyWould you please provide an Excel spread sheet of pressurizer and reactor pressure vessel temperatures and pressures for a two to three year period of time. I am performing research on nuclear power plant explosions and water hammers as they relate to nozzle damages at the Davis Besse nuclear power plant. Such information will improve nuclear safety and nuclear plant operations.'
Improving reactor explosion safety is stymied by a lack of forthcoming information.
Note that specific failure causes were never identified for Davis Besse nozzle damages. More importantly, water hammer and explosions explain such damages. Research has shown that the physics of such failures results in greater damages to piping than to pressure vessels. Nozzles are pipes.
Dynamic Stresses and Piping Failures
Dynamic load factors (DLFs) describe the equivalent effects of suddenly applied pressures to pipes and pressure vessels. DLFs are typically less than 2 for pressure vessels, and components, and short pipes. DLFs are less than 4 for longer pipes. For equal pressures, pipes experience much greater stresses to crack those pipes than would be experienced in pressure vessels, or tanks.
Water hammers cause larger DLFs, while explosions have much smaller DLFs but much greater pressures. Details to support these conclusions are available ("Fluid Mechanics, Water Hammer, Dynamic Stresses, and Piping Design", 2013, Leishear, ASME Press, pp. 1-448). Damages are further exacerbated by corrosion, which accelerates microscopic cracks that are caused by water hammers or explosions (Figure 4).

Figure 4: Microscopic crack on the inside of a steel pipe, caused by a water hammer pressure wave.
(Image by Leishear Engineering) Details DMCA
PWR Pressurizer Piping Damages
Again, quoting the NRC,
Operating experience, both domestic and foreign, has demonstrated that Alloy 82/182/600 materials connected to a pressurized water reactor (PWR) pressurizer are susceptible to primary water stress corrosion cracking (PWSCC). Most leakage events were the result of axially-oriented PWSCC of the pressure boundary portion of pressurizer heater sleeves. However, more recent events and non-destructive examination results on heater sleeves have demonstrated that circumferentially-oriented PWSCC can occur in the non-pressure boundary portion of these components ("Pressurizer Issues", click here).
Note that a specific steel material has been identified with respect to corrosion, but the NRC did not discuss the cause of failure stresses at all. Explosions explain such stress-corrosion damages to crack piping.
PWR Pressurizer Heater Damages
Pressurizer heaters are subject to cracking.
Pressurizer heaters in Nuclear Power Plants are subjected to the most severe working condition.' 'They cumulate mechanical, thermal and electrical stresses. Since the nineties, incidents of pressurizer heaters using 316L grade sheath tube in nominal primary water environment cracking have been encountered in many Nuclear Power Plants (Pressurized Water Reactor type). This kind of incident is very detrimental in heaters due to possible leakage and dissolution of the MgO in the primary coolant. Costly unplanned downtime cannot be avoided. ("Corrosion Cracking of Pressurizer Heaters in Nuclear Power Plants", Click Here.
Note that explosions were not considered by the NRC with respect to heater damages. Figures 5 and 6 provide an example of a pressurizer and pressurizer heaters.
BWR RPV Jet Pump-Assembly Failures
Structural supports for jet pumps in RPVs experienced damages due to unknown causes, where these pumps provide better heat transfer between cooling water and reactor fuel. Explosions and water hammers provide a damage explanation. Quoting the NRC,
Following vessel head removal and defueling, TV camera and visual inspections of the jet pumps and vessel annulus revealed the hold-down beam assembly of the suspect jet pump had broken across its ligament sections at the mean diameter of the bolt thread area. Failure of the beam assembly resulted in pump decoupling at the diffuser connection. Subsequent in situ ultrasonic examination of all other jet pump hold-down beams,' 'revealed ultrasonic indications of cracking at the same location in 6 of the remaining 19 beams examined. Initial estimates of crack depth ranged from 6 to 20 mils. A sketch of the typical jet pump assembly is shown in figures 1 and 2.
On March 15-16, 1980, in situ ultrasonic examination was performed on all 20 [of the] jet pump hold-down beam assemblies at Quad Cities 2.' 'One beam was found to contain a crack indication estimated to be in excess of 100 mils depth in the same location on the beam as found at Dresden.
On March 28, 1980, Boston Edison reported that ultrasonic examination revealed crack indications in three (3) hold-down beam assemblies at Pilgrim Unit 1 ("Bulletin 80-07: BWR Jet Pump Assembly Failure", Click Here, .nrc.gov/docs/ML0312/ML031280383.pdf).
Note that explosions were not considered by the NRC for jet pump support damages, and a failure cause was not cited.
Steam Turbine Damages
Since turbine damages occur in both BWRs and PWRs, fluid transients, or water hammers, may contribute to damages. Note that in BWRs, turbines may be directly subject to reactor system explosions, but in PWRs the turbines are in a different piping system, and turbine components are not directly subject to reactor system explosions. Damages to turbine discs and shafts have been observed, such that:
Turbine discs: 'Investigations were performed on a cracked turbine disc from the Cooper Nuclear Power Station (BWR), and on two failed turbine discs from the Yankee-Rowe Nuclear Power Station (PWR) ("Examination of Cracked Turbine Discs from Nuclear Power Plants", Click Here.'
Turbine shafts: 'On October 31, 2004, the inspection identified that the Unit 3 Main Turbine Generator Rotor had a crack in the shaft near the rotor coupling. 'On November 1, 2004, a crack was identified on the Unit 2 rotor shaft.' 'The root cause of these events was determined to be intermittent oscillating torsional loading on the generator rotor, which produced a torsional fatigue failure mode. The cause of the intermittent oscillating torsional loading is indeterminate ("Dresden Nuclear Power Station, Units 2 and 3 Main Turbine Generator Rotor Cracks" .nrc.gov/docs/ML0503/ML050330479.pdf).'
Water hammers and explosions are never considered during turbine failure analysis.
NRC Cover-ups are Appalling
The facts are appalling that the NRC does not know why such a wide range of dangers have occurred. Equipment is destroyed by so-called unknown causes in nuclear plants. Explosions have been observed in nuclear plants. Other explosions are expected. Nuclear plant damages are consistent with explosion damages. Explosions explain nuclear plant damages.
I do not know for certain that all of the damages discussed here were caused by explosions and water hammers. However, I do know that such damages warrant complete investigations, and investigations to date are incomplete.
To perform complete investigations, high frequency pressure transducers must be installed on RPVs and pressurizers, and elsewhere in nuclear reactor systems to measure explosions and water hammers to determine the scope of world-wide nuclear reactor design defects.
Earlier predictions of the next nuclear power plant meltdown and possible explosion before 2039 are not affected by this discussion. This discussion focuses on nuclear plant explosions during day to day nuclear reactor operations at power plants. As mentioned in an earlier Op Ed, there may be hundreds of such small explosions. Prevention of explosions, both large and small, are paramount to nuclear safety. Nuclear power plant explosions can be stopped!
Addendum
The NRC, DOE, IAEA, and NEA refuse to respond to the following email accusations. Vattenfall and the Swedish Radiation Safety Authority were also cc'd on this email. My interest in this research is to promote nuclear safety.
'Why do you permit nuclear power plant explosions? 2/15/2023
Your inaction risks lives, nuclear plant damages and damages to the environment.
Small explosions continue and large explosion disasters are at risk. Yet, your organizations refuse to act or even acknowledge the publications that are written to improve nuclear safety. Do lives have so little value?
I have sent many emails to your organizations with references from peer reviewed journals and Op Eds, which were published to the public. Based on peer reviewed journal publications, a partial list of recent accusations follows.
"Nuclear Power Plant Explosions and Damages During Normal Operations", click here.
"Ringhals 4 and the Next Nuclear Power Plant Explosion Prediction", click here.
"Nuclear Threats - Part 5 - An Incoming Nuclear Plant Explosion Disaster- Zaporizhzhia Near Missed This Next Disaster", click here.
"The U.S. Government Murders Us Through Indifference and Deceit - Cover-ups Throughout U.S. Industries", click here.
"One More Government Cover-up: The Diablo Canyon Nuclear Reactor System Explosions and Resultant Leak", click here.
"Nuclear Threats - Part 3 - Our Government Lies to Us about Nuclear Safety - Radioactive Explosions in War and in Peace", click here.
"You Can Stop an Explosive Nuclear Disaster: A Message to Nuclear Power Reactor Operators", click here.'
["Stop A Potential Radioactive Europe and Russia - A Letter To Energoatom, The Ukraine Nuclear Power Company", click here.]
(Article changed on Feb 19, 2023 at 7:36 PM EST)